What is Myopia?
The eye’s tear film, cornea and lens bend light so it focuses on the retina. The retina receives the picture formed by these light rays. It sends the picture to the brain through the optic nerve, which is actually part of the brain.
Myopia occurs when the eye is longer than normal or has a cornea that is too steep. As a result, light rays focus in front of the retina instead of on it. In this case, you see near objects clearly, but distant objects appear blurred.
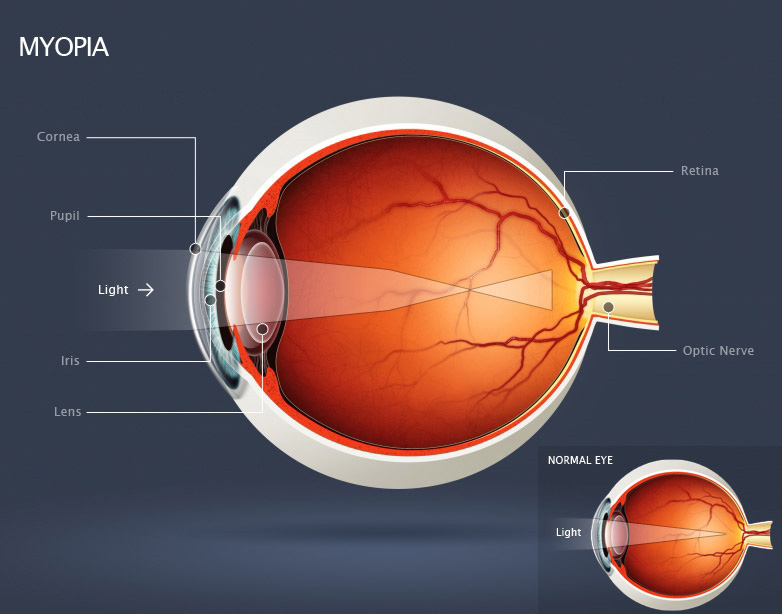
When the spherical equivalent objective refractive error is -5.00 diopters or more, then it is considered pathologic or degenerative myopia.
Why is myopia management important?
Traditionally, myopia, or “nearsightedness,” has been classified as a refractive or vision disorder, but as the prevalence of myopia has skyrocketed to become the most common ocular disorder worldwide (27% of the world’s population in 2010, 33% or 2.6 billion in 2020, and estimated to be half by 2050) and the leading cause of visual impairment in children, so has the incidence of associated pathologic conditions.
Children are becoming myopic earlier in life and to a stronger degree than in the past, especially in developed countries as they spend more time indoors using computers, looking at smartphones, and watching television. Engaging in those activities, particularly for those with myopic parents, increases their risk of developing pathologic myopia, retinal detachment, glaucoma, and cataracts.
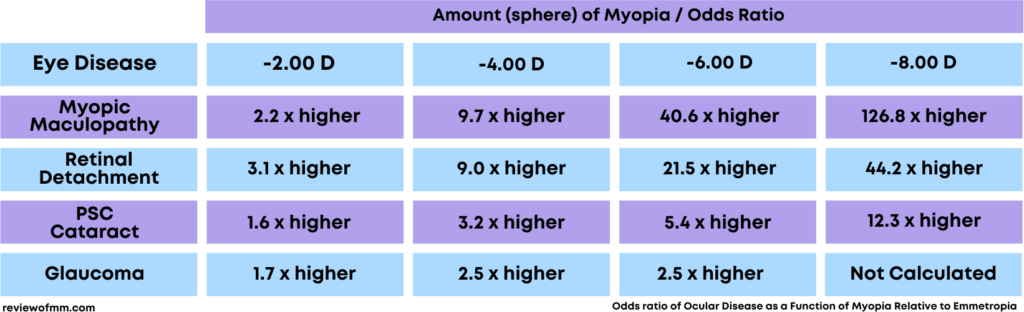
The socioeconomic impact of vision impairment due to myopia is significant. It affects patients physical, emotional, and social functioning, and the estimated costs of addressing the disease exceed US $20 billion.
- Nearly fifty percent (49%) of children with myopia experience difficulty in the classroom.
- Forty-one percent of parents with myopic children claim their children struggle with everyday activities.
- Thirty-five percent of myopic children report not enjoying school.
- Thirty-eight percent of parents of myopic children report their children have difficulty playing sports.
- Only forty-one percent of parents noticed their children were suffering from myopia.
What is myopia management?
Eye care professionals recognize the need for early intervention to control the progression of myopia rather than just continuing to passively correct the worsening refractive error.
Ongoing research indicates there are two mechanisms of action to slow the progression of myopia: biochemical influence and optical defocus. Biochemical influence involves instilling dilute atropine eye drops on both eyes every night long term and optical defocus is accomplished by wearing a specific type of soft contact lens every day or by inserting rigid, gas-permeable lenses every night to “reshape” the cornea while sleeping [orthokeratology (ortho-K)].
Low-dose atropine eye drops
Atropine is a medication that, at full strength (1%), dilates the pupil and limits accommodation. The Atropine for Treatment of Childhood Myopia (ATOM) and Low-Concentration Atropine for Myopia Progression studies have shown that a lower dose of atropine (0.01% or 0.02%) effectively limits overall myopia progression with the fewest side effects and the lowest rebound effect.
Drops are instilled on both eyes once per day until adulthood. While the drops are generally well-tolerated, side effects may include light sensitivity secondary to mild pupillary dilation, blurry vision associated with loss of accommodation, eye irritation, allergic conjunctivitis/dermatitis or rebound nearsightedness. Because atropine 0.01%/0.02% eye drops are not currently commercially produced, they must be obtained from a compounding pharmacy. Pricing for the eye drops vary by compounding pharmacy. Unfortunately, they are not usually covered by medical or vision insurance.
Soft multifocal contact lenses
The use of soft contact lenses for myopia control dates back to the 1970s with varying levels of success. More recent studies have investigated the use of soft/soft toric center-distance multifocal contact lenses with a peripheral near-vision zone. The center-distance portion of the lens corrects the wearer’s vision while the peripheral near-vision zone reduces or eliminates peripheral hyperopic defocus (in favor of myopic retinal defocus), which is thought to cause myopic progression.
CooperVision’s MiSight (daily), Proclear (monthly), and Biofinity (monthly) multifocal (MF) contact lenses are used for myopia control based on the peripheral hyperopia theory. The center-distance portion of the lens which corrects myopia is surrounded by optics that cause myopic defocus in the peripheral retina, so eyes do not elongate as readily. In studies, MiSight MFs slowed progression of myopia by 3% in >10 months and 59% over 3 years, Proclear MFs slowed myopia progression by 51% over 2 years, and Biofinity MFs with +2.50D [used in the BLINK (Bifocal Lenses In Nearsighted Kids) study] yielded 43% slower myopia progression and 36% slower axial length growth over 3 years.
Contact lenses must be worn for a certain number of hours every day to achieve optimal results though pupil size may interfere with the efficacy of treatment. Young children may have difficulty with lens insertion and removal and contact lens wearers are at increased risk of developing corneal diseases, which could be vision-threatening.
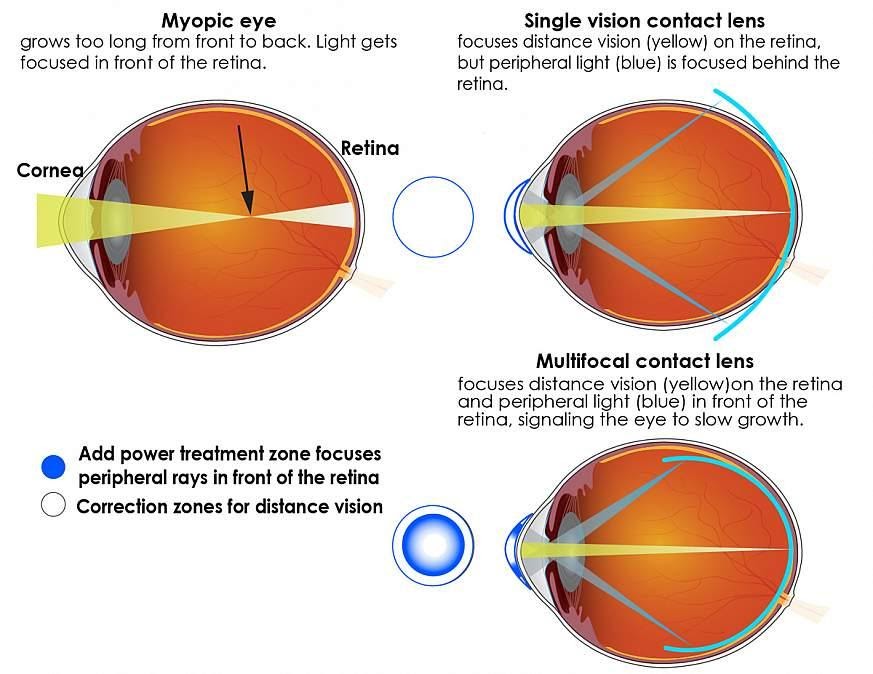
National Institutes of Health – Multifocal contact lenses slow myopia progression in children
Orthokeratology (Ortho-K)
Also known as corneal reshaping, this method involves wearing rigid, gas-permeable lenses overnight to temporarily flatten the cornea. This treatment does not yield a permanent effect. If your child stops wearing Ortho-K Lenses regularly during sleep, your child’s vision may return to its original state in as little as 72 hours.
One pair of Ortho-K lenses can cost $1,000.00-$2,000.00 plus the cost of the contact lens fitting and follow up visits.








